BACTEK – R modo de uso
MEJORA LA INMUNIDAD A NIVEL SISTÉMICO ESPECIALMENTE VÍA AÉREA Y TRACTO DIGESTIVO
DISMINUYE LA FRECUENCIA DE INFECCIONES VIRALES Y SOBRE INFECCIONES BACTERIANAS
ACTIVA TODAS LAS CÉLULAS DE DEFENSA Y MEJORA SU DESEMPEÑO
AUMENTA LAS MOLÉCULAS Y ANTICUERPOS CIRCULANTES DE DEFENSA EN LA VÍA AÉREA Y TRACTO DIGESTIVO COMO IGA SECRETORA (primera línea de defensa especifica en mucosas)
ACTUÁ EN LA INMUNIDAD ESPECIFICA, PROMUEVE LA RESPUESTA NORMAL (TH1)Y DISMINUYE LA ALÉRGICA (TH2)
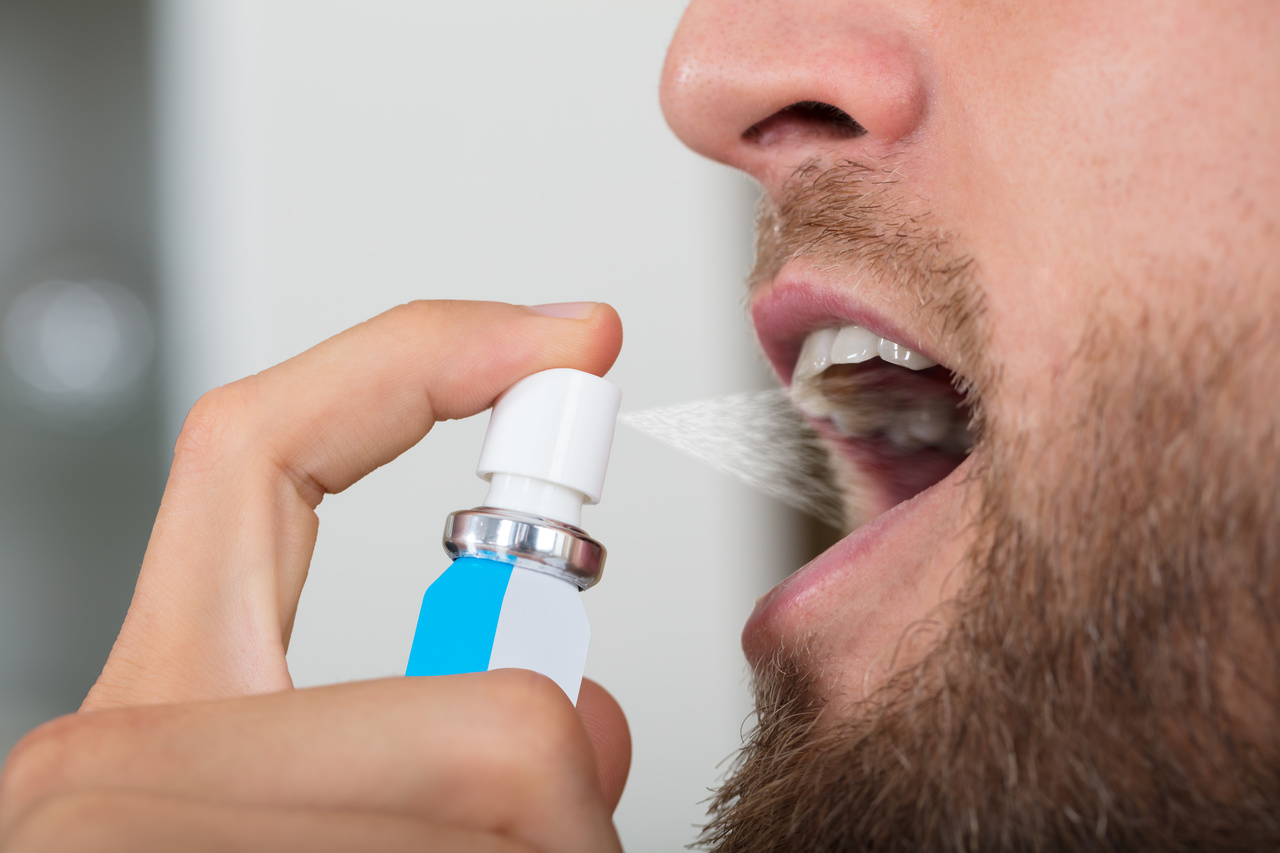
PRESENTACIÓN Y MODO DE USO:
Una caja trae dos frascos, se aplica a modo de espray
2 aplicaciones al día Sublingual en ayuna mantener en la boca un minuto y deglutir, tiene sabor a piña agradable para niños.
Esperar treinta minutos antes del desayuno.
Cada frasco dura un mes y medio, se debe guardar en el refrigerador lejos del Freezer.
El efecto en la inmunidad se alcanza en su totalidad en dos semanas
Solo suspender en caso de un cuadro febril mientras dure esta y luego reiniciar.
Prácticamente sin efectos adversos, solo evitar en pacientes con enfermedades autoinmunes, inmunodeficiencia (cáncer-sida) o tratamientos con inmunosupresores.
ES LA MEJOR ALTERNATIVA EN AUMENTAR LA INMUNIDAD Y DISMINUIR LA ALERGIA.
Referencia bibliográfica:
- Ememerich et al. Influence of BIM on different humoral and celular defense mechacnismns of the respiratory tract. Respiration 1992; 59; 19-23
- Mauel J. Stimulation of inmunoprotective mechanismsby BIM. A review of results from in vivo and in vitro studies. Respiration 1994; 61 ; 8 -15
- Keul et al. Induction of interleukin 6 and interleukin 8 expression by BIM via C-Fos/serum responsive element. Thorax 1996; S 1 : 150-154
- Roth, Block. Distinct effects of BIM on gp binding cytokines. Thorax 2000; 55: 678-684
- Quezada et al. Efects of bacterial antigen on IgG an IgA levels in children with recurrent infections and hipogamaglobulinemia Invest Allergol Clin Inmunol 1999; 9 : 178-182
- Navarro et al. the oral administration of bacterial extracts prevents asthma via the recruitment of regularoratory T cells to the airways. Mucosal Inmunonology 2011
- Huber et al. Th1 orientated inmunological properties of the bacterial inmunity. Eur J Med Res 2005; 10: 209-217
- Parola et al . Selective activation of human dendritic cells by BIM trough a NF-kb and PAMPS depeneded the pathway. Plos One 2013; 8 : e 82867
- Fu et al BIM attenues allergic airway inflammation by restoring GSK# B-related T regulatory cells insufficiency. Plos One 2014; 9 e 92912
- Han et al. A bacterial inmunotheraphy prevents rhintis in mice. Am J Rhinol Allergy 2014; 28: 110-116
- Lu et al. Bacterial theraphy increases de percententage of natural Killers T cells in peripheral blood and alleviates asthma in children. Pharmacology 2015; 95: 139-144
- Ciceran A. Inmunologia del anillo de Waldeyer. III Manual de Otorrinolaringologia pediátrica. IAPO Santiago de Chile 2003
- Brandtzaeg et al. Terminology, nomeclature of mucose associated lymphoid tissue. Mucosal Inmunology 2008
- Schraml et al. Regulatory T cells . Mechanisnms of differentiation a function. Annu Rev Inmunol 2012. 531-564
- Cella et al . Beyond NK cells, the expanding universo of inhale lymphoid cells. Frontiers in inmumonolgy 2014, art 282.
- Wybran et al . Activation of natural killer cells and cytokine productions in humans by bacterial lung, 1990. 720-725.
